SUNWAY DIPLOMA STUDIES DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING DIPLOMA IN FINANCE DACC AND DFIN Semester Student Name. Subordinate courts consist of the Sessions Court the Magistrates Court and Penghulus Court.

Malaysian Criminals Go To Different Courts Depending On Asklegal My
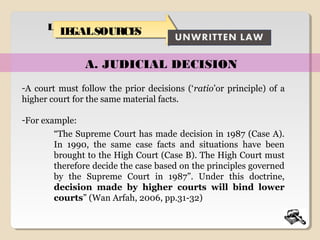
It is only vested with one jurisdiction which is the Appellate jurisdiction.
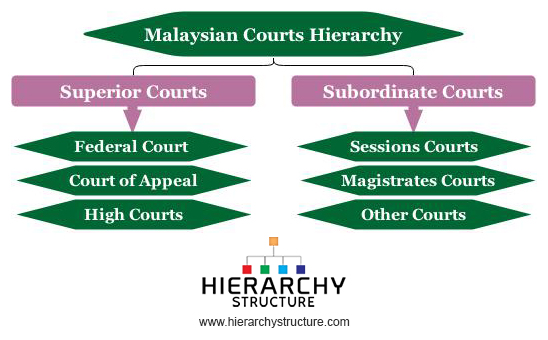
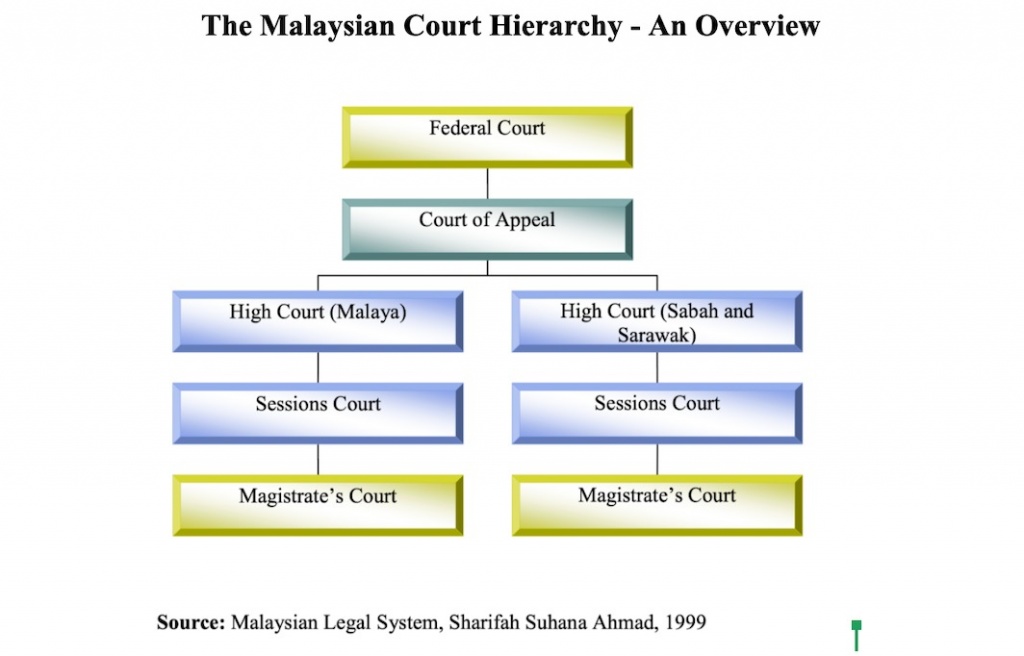
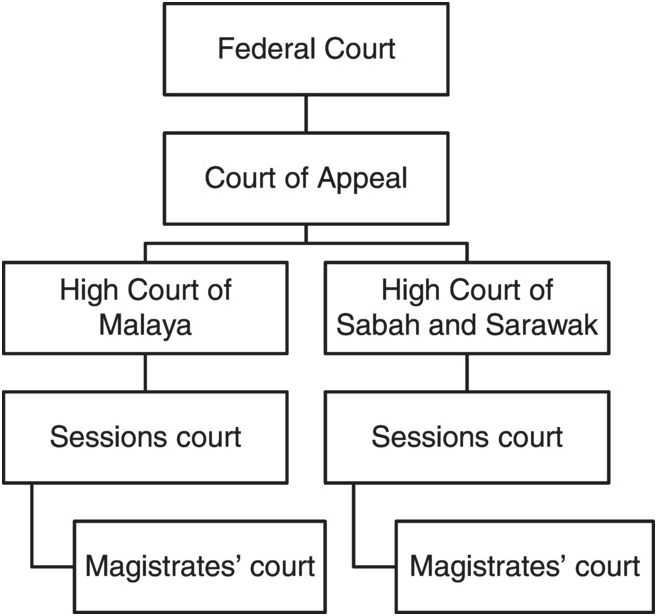
. INTRODUCTION The hierarchy courts of Malaysia starts with the Magistrates Courts as the first level follow by the Court of Appeal High Court Session Court and the Federal Court of Malaysia which is the highest level. The Court of Appeal is the second highest court in Malaysia and is vested with only one jurisdiction that is Appellate Jurisdiction. Amount in dispute in any civil matters must exceed RM10000 except where it involves a question of law.
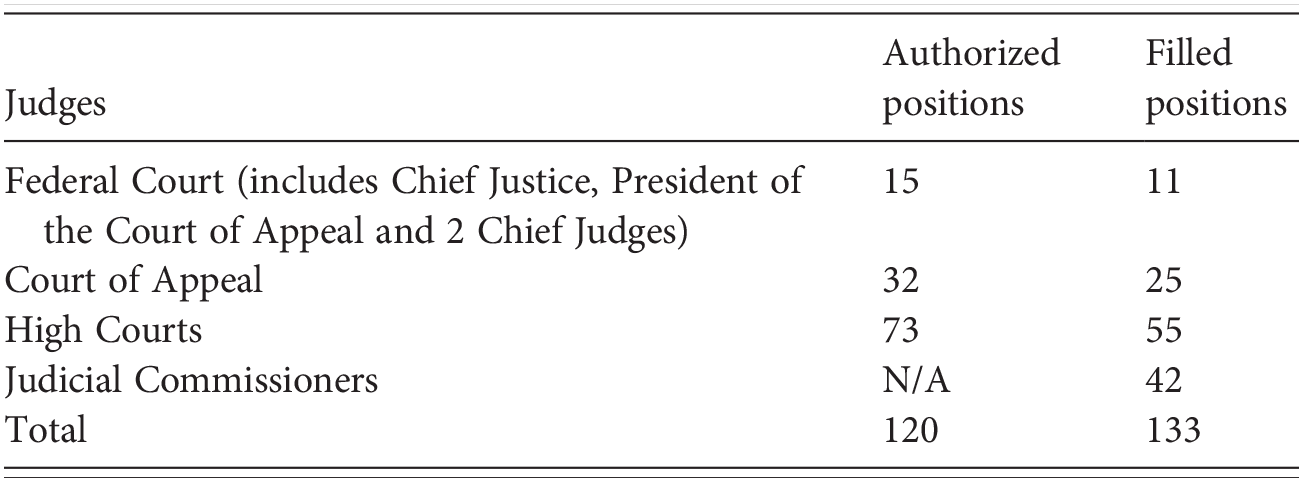
The second is in Sabah and Sarawak which has eleven judges and judicial commissioners. Outside the court hierarchy are the Syariah Courts Penghulus Courts and the Native Courts. Tribunals may resemble courts as they are administrative and have someone who takes up the role of a judge to hear the case but it is not recognised as a court that will have to follow the standard judicial system.
The court of Appeal is an appellate court of the judiciary system in Malaysia and has jurisdiction to hear appeals against any High Court decision relating to criminal matters. Commercial matters although to a lesser extent are also heard and dealt with in other parts of Malaysia where the High Courts enjoy local jurisdiction 1. High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are.
The hierarchy of courts begins from the Magistrates Court Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and finally the Federal Court. The Commercial Courts are situated in Kuala Lumpur. The High Court.
There are generally two types of trials criminal and civil. The Federal Court of Malaysia in the highest court of the land. At present there are eighty seven Sessions Court judges throughout Malaysia.
B Interest shall be computed daily to the date of payment except as provided in section 2516b of this title and section 1304b of title 31 and shall be compounded annually. The first is in Peninsular Malaysia which contains forty-five judges and judicial commissioners. A tribunal is basically a body established to settle certain types of dispute.
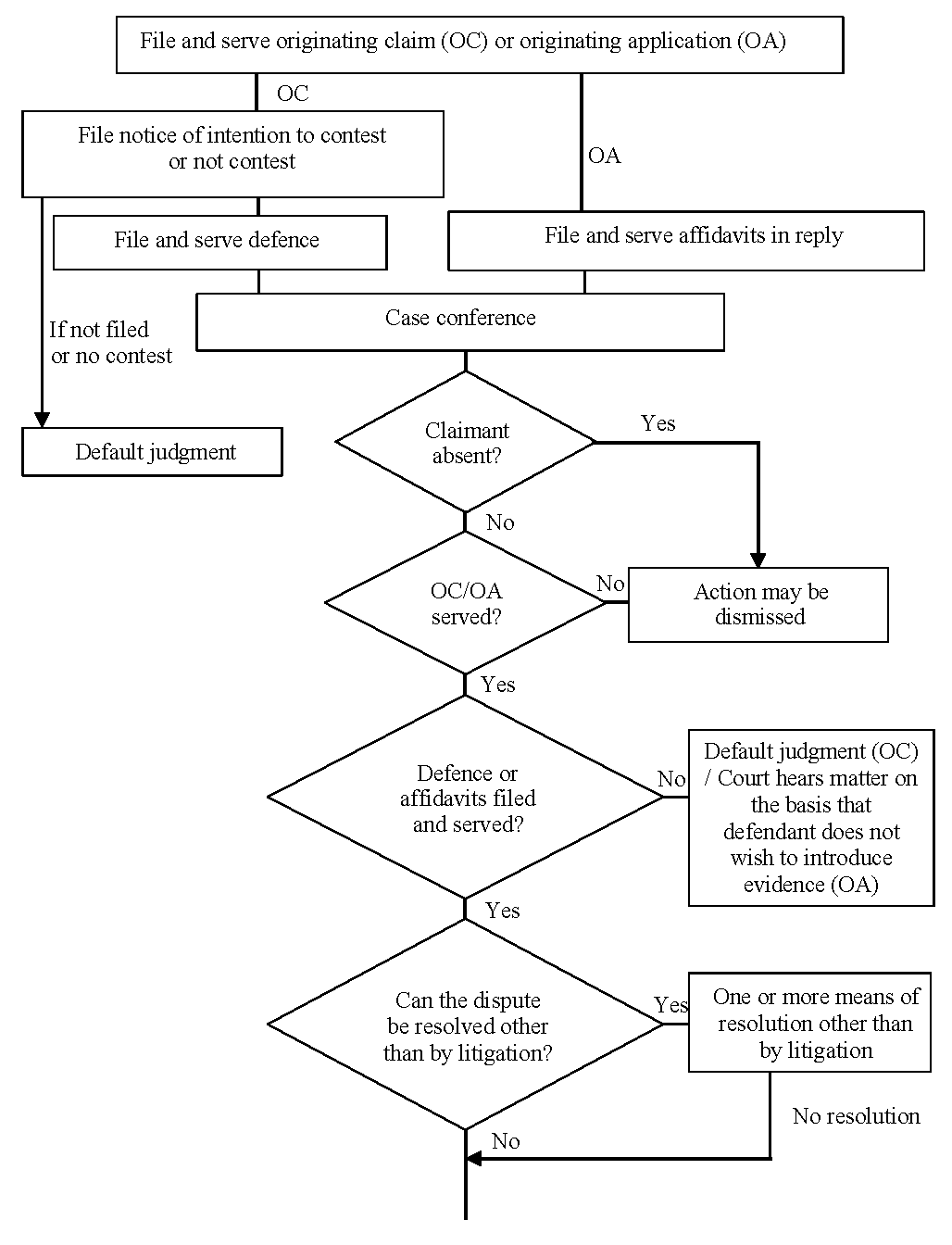
Case management which is largely undertaken by the judges is a central feature that enhances the performance of these courts. Vested with only ONE 1 jurisdiction For criminal cases any criminal appeals against any decision made by the High Court can be heard by the Court of Appeal under S. Beyond having a hierarchy the courts are also divided into courts of first instance and appellate courts.
A Sessions Court has the jurisdiction to hear both criminal and civil cases. COURT OF APPEAL The Court of Appeal is established by Art 121 1B of FC and is the second highest court in Malaysia. A Sessions Court judge is appointed by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong on the.
The High Courts in Malaysia are the third-highest courts in the hierarchy of courts and there are two chief judges in the High Court. The court systems are built in a hierarchal system in order to facilitate the hearing of cases and any appeals against them. 50 of CJA 1964.
The High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are superior courts. In civil matters also the court of Appeal has jurisdiction to hear and determine. Courts of first instance.
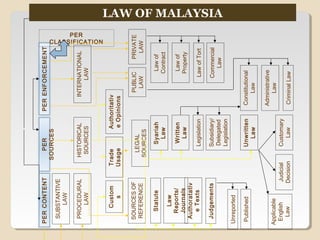
View Types of Courts in Malaysiadocx from BUSINESS LAW at Sunway University College. Tribunals are not heard by judges to begin with. The jurisdiction of the courts in civil or criminal matters are contained in theSubordinate Courts Act 1948 and the Courts of Judicature Act 1964.
Courts of first instance are where matters are heard for the first time. 28 rows The high courts in Malaysia are the third-highest courts in the hierarchy of courts after the Federal Court and the Court of AppealArticle 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two high courts of co-ordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak before 1994 the High Court in Borneo. The Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts.
The Sessions Court may also hear other matters where the amount in dispute does not exceed RM1000000. Under Appellate Jurisdiction for criminal appeals Section 501 of Act 91 provides that the Court of Appeal has jurisdiction to hear and determine any criminal appeals against any decision made by the High Court. A Sessions Court may hear any civil matter involving motor vehicle accidents disputes between landlord and tenant and distress actions.
Malaysian Courts Hierarchy Chart Hierarchystructure Com
Courts In Malaysia And Judiciary Initiated Reforms Chapter 11 Asian Courts In Context
The Malaysian Court Hierarchy A Review Of Malaysia S Civil And Criminal Court Hierarchy Richard Wee Chambers

You Can Make An Appeal If You Lose Your Case In Asklegal My
Hierarchy Of Courts For Civil Cases In India Civil Law India

Umlr University Of Malaya Law Review Lex In Breve

Malaysian Criminals Go To Different Courts Depending On Asklegal My

Appellate Intervention When Can The Appeal Courts Step In Malaysian Litigator

The Malaysian Court System Asklegal My

Rules Of Court 2021 Singapore Statutes Online

Role And Structure Of The Supreme Court Structure
Advantages Of Court Hierarchies
Courts In Malaysia And Judiciary Initiated Reforms Chapter 11 Asian Courts In Context

Malaysian Criminals Go To Different Courts Depending On Asklegal My